Body Shapes of Soccer players
come in a variety of physical shapes and sizes, and there are no strict rules regarding body type for any position. While goalkeepers, central defenders, and target forwards tend to be taller and heavier, there are many exceptions in every position.
Generally, soccer players are known for their lean muscular build and strong, toned legs. They tend to have an average height similar to that of the general population, and their weight is typically below 200 lbs for men and 155 lbs for women.
These physical attributes are largely a result of the high level of cardiovascular fitness and endurance required to play professional soccer. However, it’s important to note that body type and physical characteristics are just variables, and a player’s skills and abilities are ultimately what determine their success on the field.
Body Shapes of Soccer Players
From a scientific standpoint, there are three different body types [Physical Built]:
- Ectomorphs
- Mesomorphs
- Endomorphs
Below is a table outlining the various body types that are commonly observed in soccer, along with their potential benefits on the field. This information can be useful in understanding how body type can play a role in a player’s performance.
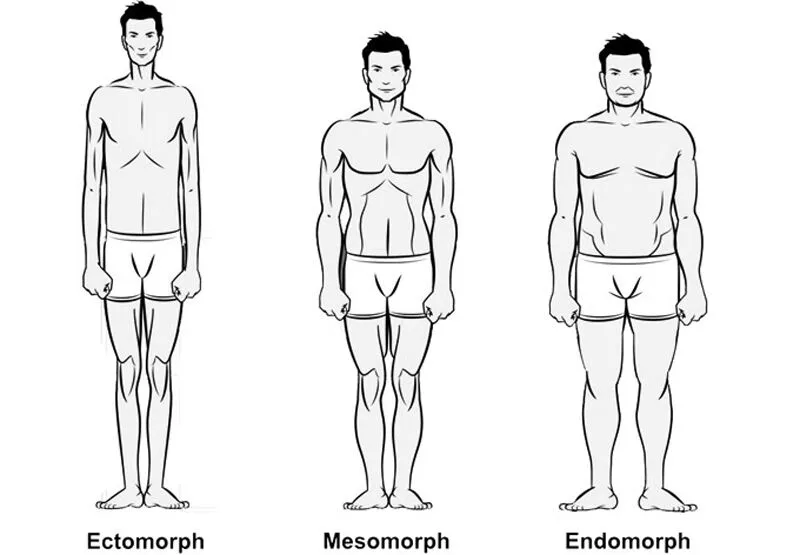
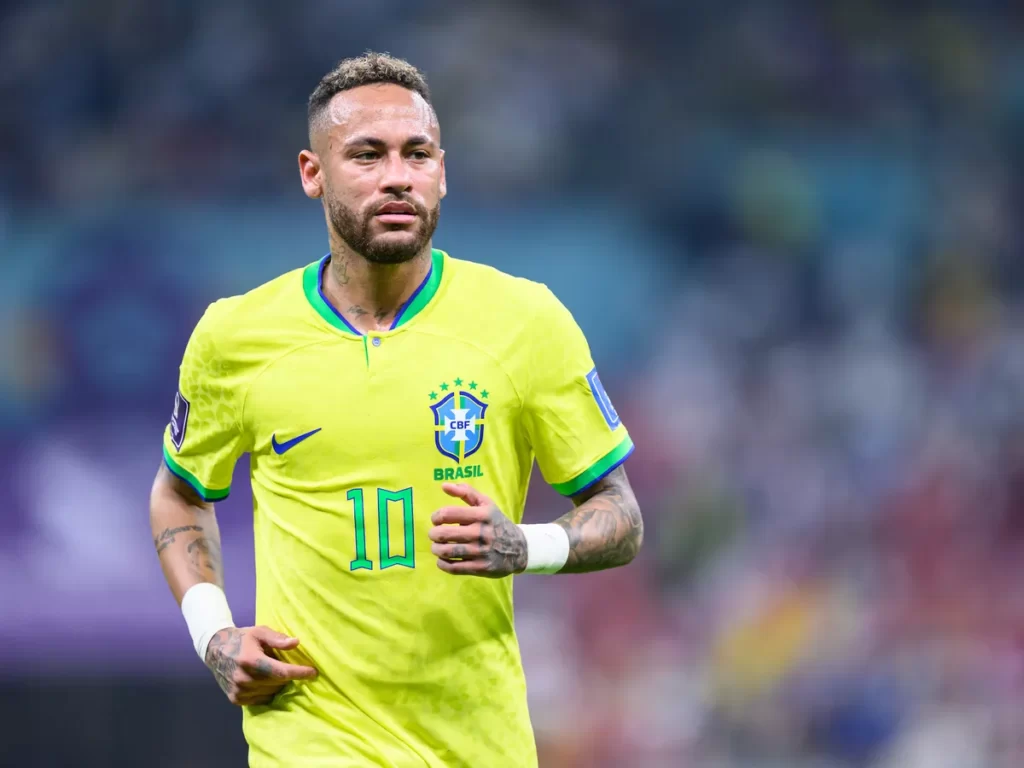
1. Ectomorph:
The ectomorph body type is prevalent among athletes, characterized by a slender and elongated build, often accompanied by above-average height. This body type provides an advantage in areas such as heading the ball during corner kicks and goalkeeping due to their height. Their lightweight build also allows them to be quick on their feet.
However, their frail physique can be exploited by opposing players, making them vulnerable to physical contact on the field. Due to their lack of muscle mass, ectomorphs may struggle with shielding, tackling, and blocking shots and crosses when defending.
To overcome these weaknesses, ectomorphs must learn to optimize their speed and develop effective techniques for winning possession of the ball against stronger players.
Prominent Ectomorphs Soccer Player Bodies – Lionel Messi, Neymar, Petr Čech.


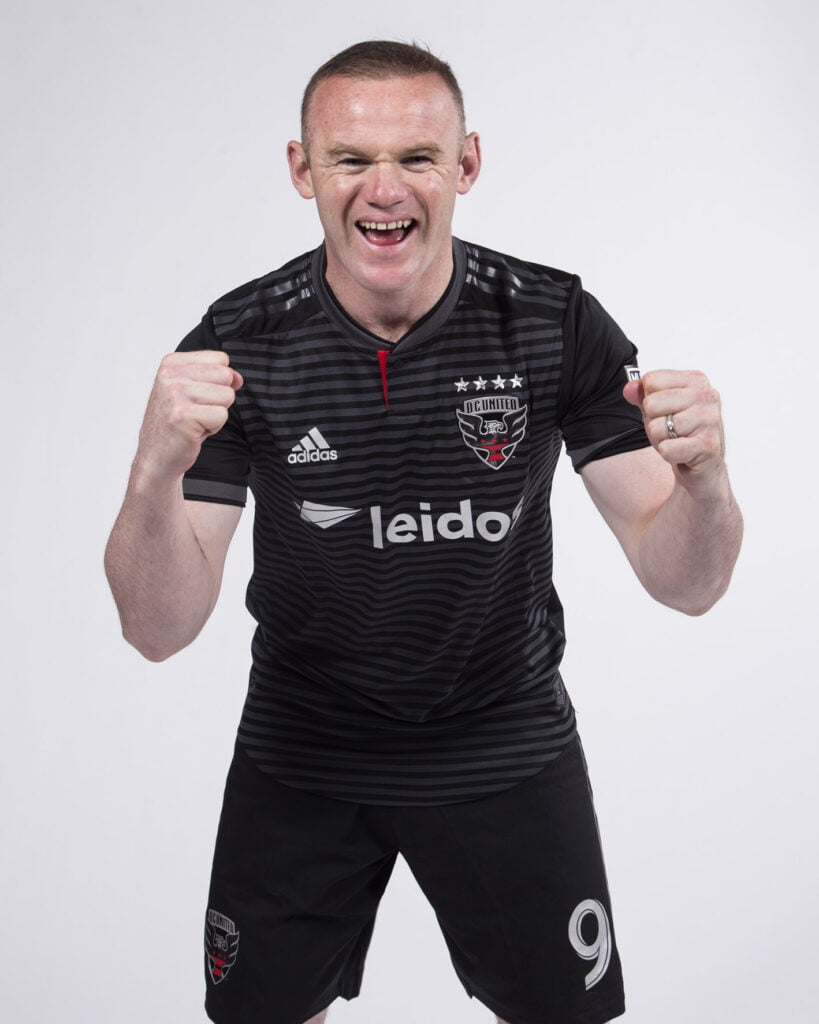
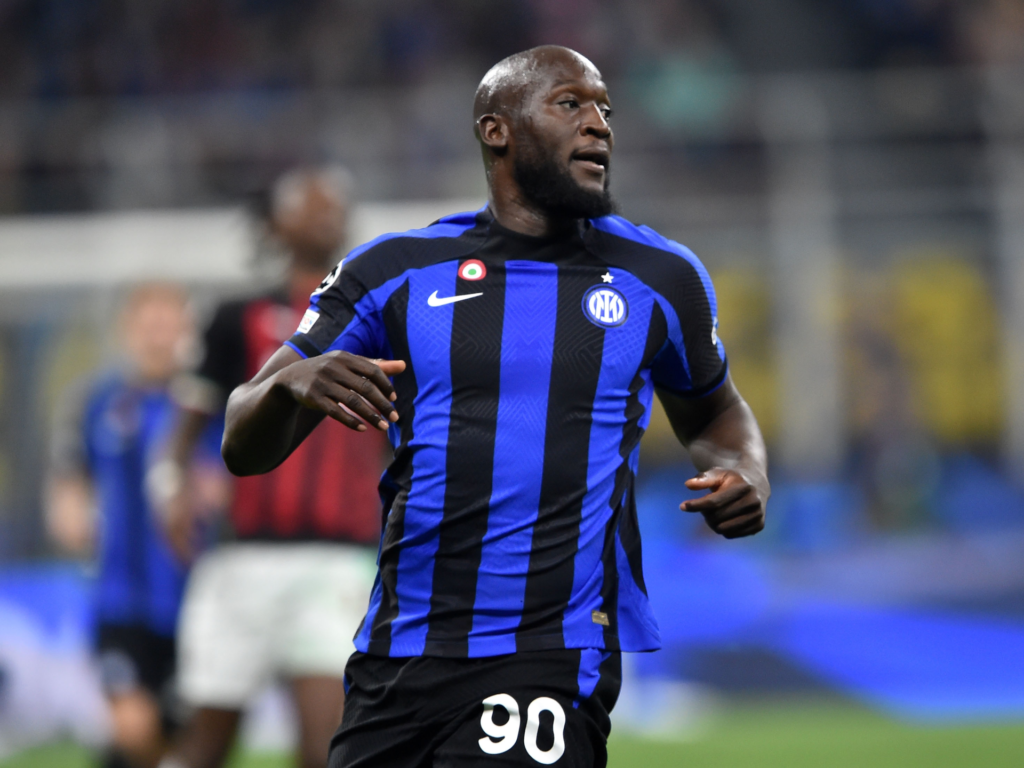
2. Endomorph:
The endomorph body type is in contrast to the ectomorph body type, characterized by a more rounded and heavier physique, with a lower metabolic rate.
Due to their slower metabolism, endomorphs may gain weight more quickly than other body types, as their bodies take longer to use up the calories they consume. This can create low-level stress in their system, which triggers the production of serotonin in their brain. This chemical helps regulate mood and appetite, and vigorous exercise can further increase its production.
However, endomorphs may struggle to keep up with faster players on the field and may face challenges in areas such as stamina and endurance.
Prominent Endomorphs Soccer Player Bodies – Adebayo Akinfenwa, Wayne Rooney, Romelu Lukaku.


3. Mesomorph
In soccer, individuals with a mesomorph body type are typically muscular and lean, with low levels of body fat and high levels of muscle mass. This body type is widely considered to be the ideal for soccer players, as it provides a combination of strength, speed, agility, and endurance that is difficult to match. As a result, mesomorphs often excel as competitors due to their well-rounded physical abilities.
Prominent Mesomorph Soccer Player Bodies – Cristiano Ronaldo, Sergio Ramos, Alexandre Lacazette.
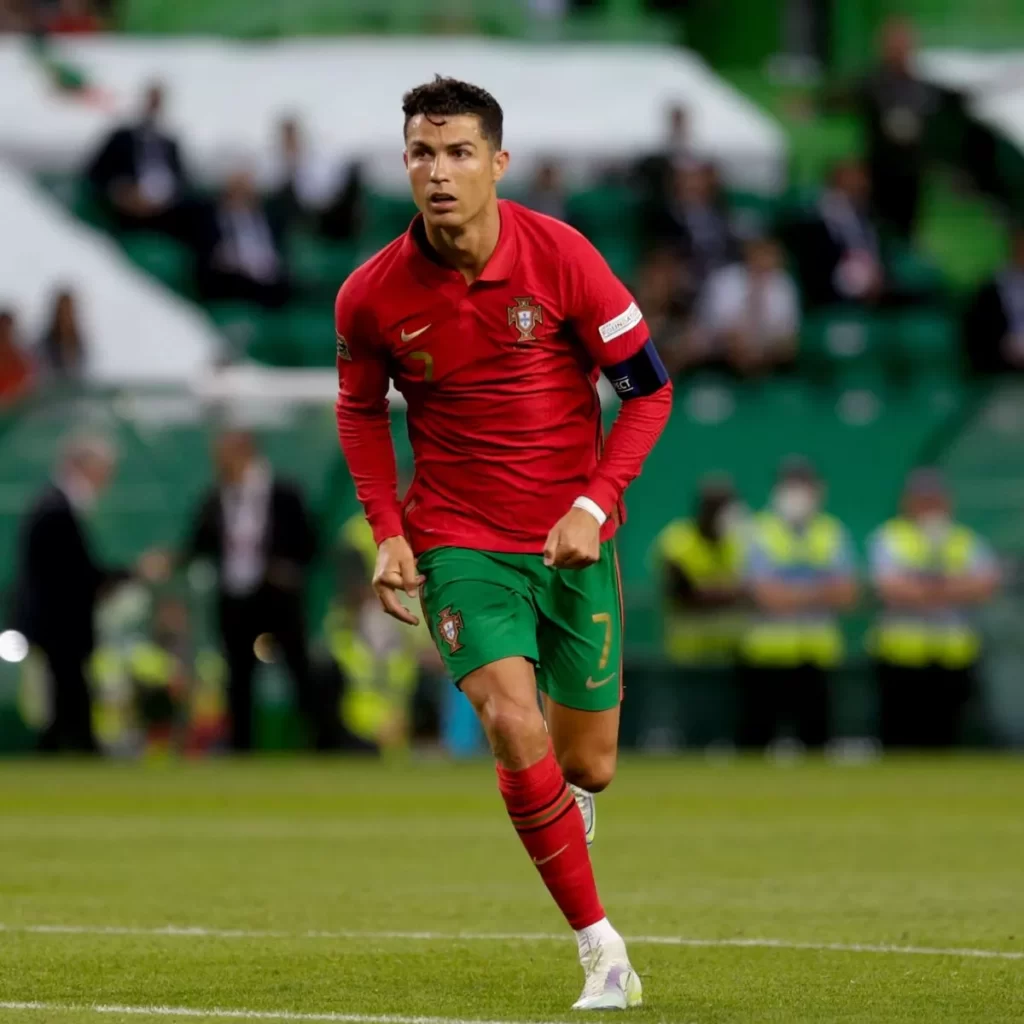
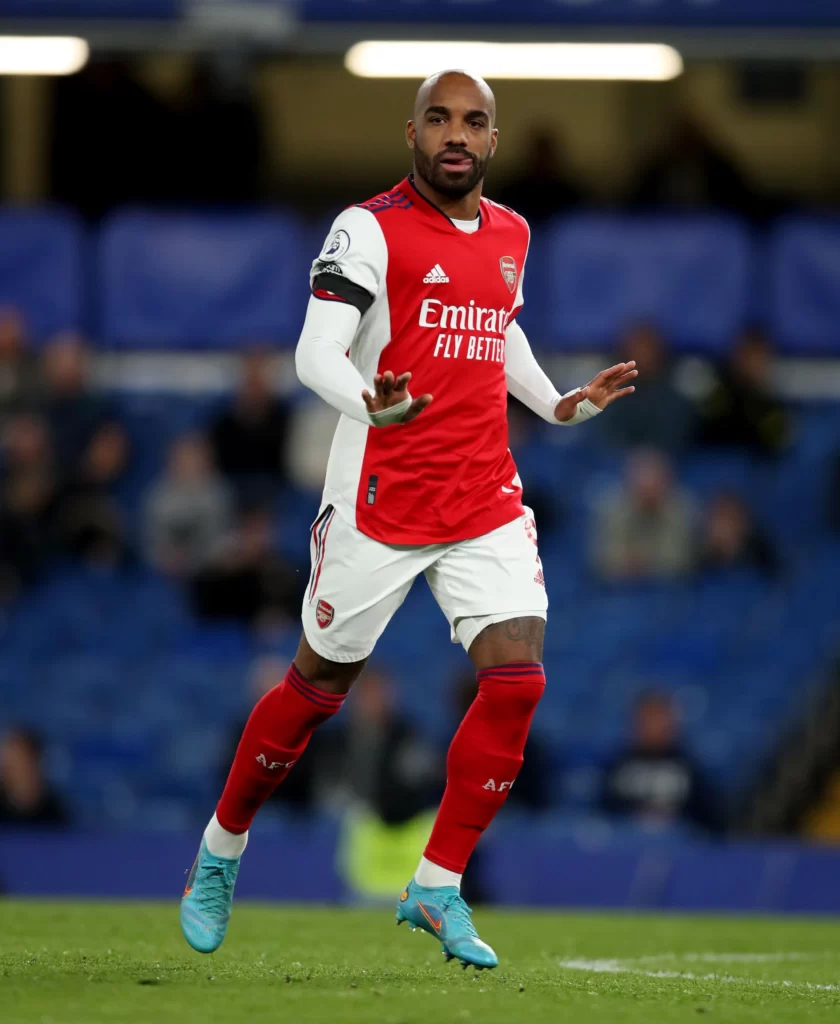


Players can change their body?
players can modify their bodies through training, nutrition, and lifestyle choices. While individuals have different genetic predispositions and limitations, they can work towards achieving specific body goals and improving their physical attributes.
- Strength and Muscle Development: Players can engage in strength training programs to build muscle mass, increase strength, and improve power. This can involve weightlifting, resistance exercises, and targeted workouts for specific muscle groups.
- Speed and Agility: Players can undertake speed and agility training to enhance their quickness, acceleration, and change of direction. This often includes sprinting drills, plyometric exercises, and agility ladder work.
- Endurance and Conditioning: Improving endurance and overall fitness levels can be achieved through cardiovascular exercises such as running, cycling, and interval training. This helps players maintain a high level of performance throughout matches and endure the physical demands of the game.
- Body Composition: Nutrition plays a crucial role in body composition. Players can work with sports nutritionists to develop meal plans that support their training goals. By maintaining a balanced diet, players can reduce body fat, increase muscle mass, and optimize their performance.
It’s important to note that changing one’s body composition takes time, dedication, and consistency. Professional players often work closely with fitness coaches, nutritionists, and medical staff to ensure they make informed decisions and avoid injury.
While players can make improvements in their physical attributes, it’s also worth mentioning that some aspects of body type, such as bone structure or height, are determined by genetics and may be less malleable. Nonetheless, with the right training and lifestyle choices, players can optimize their physical abilities to excel in their respective positions.
Which Is The Best Body Type For Soccer Players?
There is no single “best” body type for soccer players as success in the sport is determined by a combination of various factors, including skills, tactics, mentality, and teamwork. Soccer is a diverse and dynamic game that requires players with different body types and attributes to fill different positions and roles effectively.
While certain body types may provide advantages in specific positions, it is important to note that successful soccer players come in various shapes and sizes. Players like Lionel Messi, who is shorter in stature, and Cristiano Ronaldo, who has a more muscular build, have both achieved great success in the sport.
Instead of focusing on a specific body type, it is more important for players to develop and optimize their individual strengths, skills, and attributes. Players should work on enhancing their technical abilities, tactical understanding, and physical attributes such as speed, agility, endurance, and strength to reach their full potential.
Moreover, soccer is a team sport that emphasizes collaboration and collective effort. The effectiveness of a player is not solely determined by their body type but also by their ability to work well within a team, understand tactics, and make intelligent decisions on the field.
Ultimately, the “best” body type for a soccer player is one that allows them to perform optimally based on their position, style of play, and personal strengths. Emphasizing overall fitness, skill development, and a strong work ethic will generally contribute more to a player’s success than focusing solely on body type.
Important Body Attributes For Soccer
In soccer, certain body attributes can significantly impact a player’s performance and effectiveness on the field. While skills, tactics, and teamwork are crucial, the following body attributes are generally considered important in soccer:
- Speed: Having good speed allows players to outrun opponents, make quick sprints, and cover ground efficiently. It enables players to create scoring opportunities, track back on defense, and recover quickly during transitions.
- Agility and Balance: Agility refers to the ability to change direction rapidly and smoothly. Players with good agility can navigate through tight spaces, evade defenders, and maintain body control while executing quick movements. Balance is also crucial for stability and maintaining control during dribbling, turning, or challenging for the ball.
- Stamina and Endurance: Soccer matches require players to perform for extended periods, often with intermittent bursts of high-intensity activity. Good stamina and endurance allow players to maintain a high work rate throughout the game, both offensively and defensively. Players with better endurance can sustain their performance level and avoid fatigue as the match progresses.
- Strength and Power: Soccer involves physical battles, shielding the ball, and competing for aerial duels. Strength and power contribute to a player’s ability to hold off opponents, win challenges, and maintain possession. Strong leg muscles also aid in shooting power and long-range passing.
- Flexibility: Soccer requires a wide range of movements, including stretching to reach for a ball, executing high kicks, and performing quick turns. Adequate flexibility helps prevent injuries, improves agility, and allows players to execute skills effectively.
- Coordination and Body Control: Soccer involves precise footwork, dribbling, and ball control. Good coordination allows players to execute technical skills with accuracy and timing. Body control, including spatial awareness and proper body positioning, helps players make accurate passes, receive the ball well, and maintain balance in challenging situations.
It’s worth noting that while these attributes are important, soccer is a game that values a combination of physical, technical, and tactical skills. Players with different body types and attributes can excel in different positions and roles on the field, so versatility and adaptability are also valuable qualities.

![Body Types or Body Shapes of Soccer Players [Explained] - Seif Khaled](https://seifkhaled.me/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Body-Types-or-Body-Shapes-of-Soccer-Players-Explained-1.webp)
Published by